[304-3]
The protected areas, including the protection range, refuges and biological reserves, perform the function of ecological corridors because they are connected, to the south, with the Iguaçu National Park and, to the north, with the National Park of Ilha Grande. It also covers conservation units in Paraguay (Bertoni Museum) and in the Argentine province of Misiones, in addition to the Iguazú National Park.
The implantation of biodiversity corridors is an action that seeks to interconnect the isolated natural areas with the destruction of the original forests in the border region between Brazil, Paraguay and Argentina. These corridors allow the dispersion of the genes of flora and fauna, and neutralize the island effect, which compromises the diversity of species and the risk of extinction.
The Brazilian forest nursery is one of the conservation and recovery initiatives. There are produced seedlings of 75 species of native trees, with emphasis on the peroba (Aspidosperma polyneuron), the purple ipê (Tabebuia Avellaneda), the cedar (Cedrela fissilis), the ivory wood (Balfourodendron riedeliamum) and the fistula cane (Peltophorum dubium). They are seeds of high quality and high degree of genetic variability, resulting from a pioneering research initiated in 1991.
The Piracema Channel, an initiative of the Biodiversity Our Patrimony program, restored a pathway for genetic flow among fish populations fragmented by the plant bus, allowing the migratory species to overcome the 120 meters of the average unlevel of the dam and reach the breeding areas in the upper Paraná River Plain and Ilha Grande National Park.
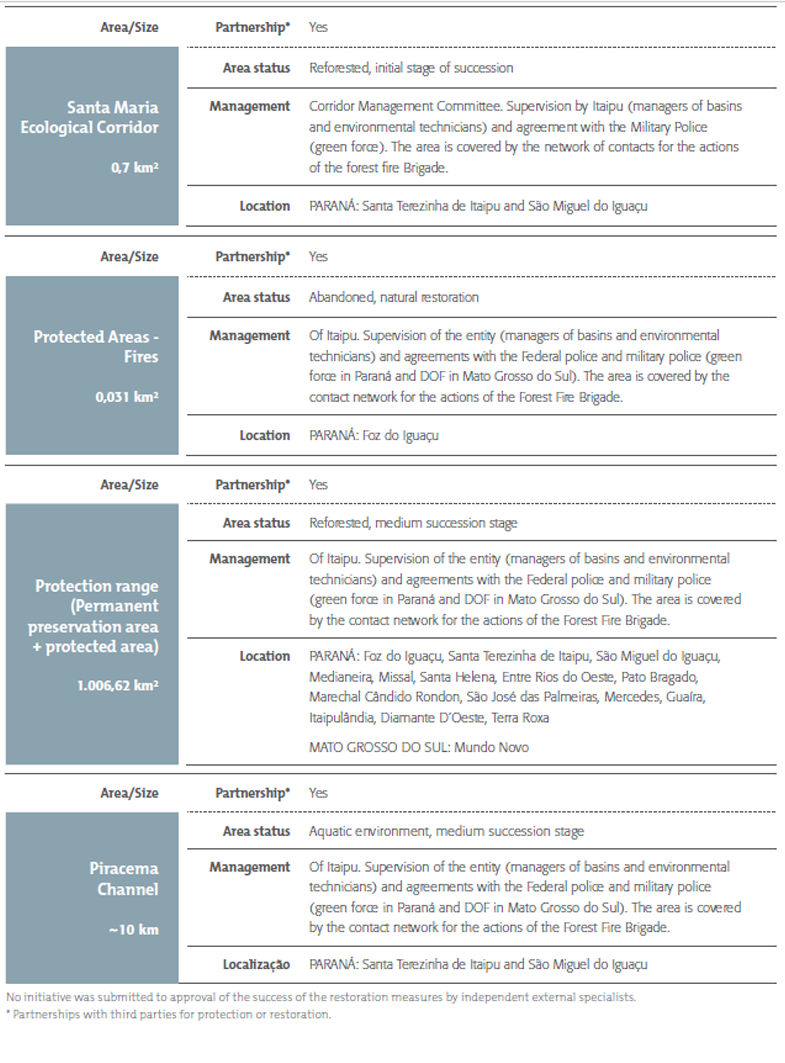
Protected or restored habitats
[304-3]No initiative was submitted to approval of the success of the restoration measures by independent external specialists.
* Partnerships with third parties for protection or restoration.


 Português
Português
 Español
Español